Spleen
What is Spleen & Location of Spleen
Spleen is one of the largest organs of the lymphatic system. It is located on the top left side of the abdomen and sits below the diaphragm and near to the stomach.
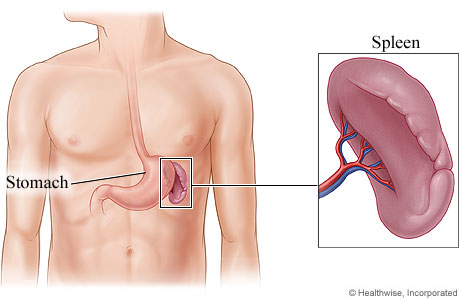
Figure 1 – Location of Spleen (where is Spleen Located)
A healthy spleen is approximately 10 to 12 cm long. Splenic capsule is a tissue that protects the spleen against injury. The spleen consists of red and white pulps. The white pulp manufactures and develops immune cells and blood cells. Red pulp purifies blood and removes dead and old blood cells. 1
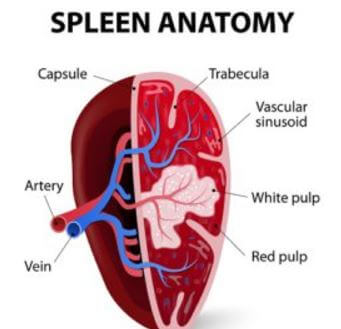
Fig 2 – Spleen Surface Anatomy
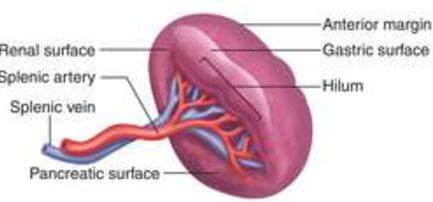
Fig 3 – Spleen Surface Anatomy 2
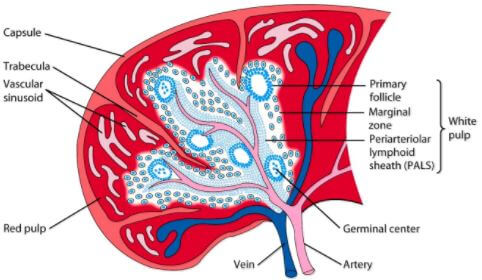
Fig 4 – Spleen Cut Section view
Functions
Spleen performs the following functions in your body:
- Spleen helps in filtering and purifying blood. It removes unwanted materials and abnormal cells in the blood.
- Protect the body against infections. The spleen takes part in the primary role of your immune system by defending the body against bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites and other unfamiliar particles.
- It produces antibodies, lymphocytes and macrophages. It also destroys red blood cells after they have functioned for an average of 120 days. The spleen also eliminates old mutated platelets from the bloodstream.
- Spleen keeps blood. It is elastic and can expand to keep large amounts of blood. When the body is in need of blood, the spleen can maintain the volume of blood in the body by moving surplus plasma from your blood into the lymphatic system.
- In particular diseases such as anemia and leukemia, it starts again to manufacture blood cells. This function occurs before a child is born.
Spleen Problems
Your spleen can become enlarged, a condition known as splenomegaly. As the spleen continues to increase in length, it can easily rapture and bleed internally which is a threat to your life. Splenomegaly can occur due the following:
Fig 5 – Enlarged spleen
Infections
Several infections caused by bacteria, viruses and parasites can affect your spleen. They include:
Endocardiac
This is an infection caused by bacteria present in your mouth. It is a serious heart infection. These bacteria affect your tooth and spreads to the gum causing bleeding.
The bacteria can enter your blood and spread to other parts of your body including the spleen and cause infections.
Diseases
Many diseases can affect your spleen. They include:
Sickle cell anemia
This is an inherited disease that alters the normal red blood cells size and shape. Normally, healthy red blood cells circulate easily in your blood transporting oxygen around your body.
Once these cells become abnormal, they can get jammed and obstruct blood cells and interfere with supply of oxygen in the body. This can also damage your spleen and other organs in the body.
Liver diseases
These are a number of diseases that affect the normal functioning of the liver. They include:
Cirrhosis
This condition causes permanent scarring of your liver. It occurs due to consuming excess alcohol for a long time. Normally, the liver breaks down alcohol and toxins in the body.
When alcohol becomes excess in the body, the liver cells are overworked and eventually get damaged.
As a result, the spleen is also damaged due too much unwanted materials in the blood. Other causes of cirrhosis include Hepatitis C, which is a blood infection.
Inflammatory diseases
These occurs when the immune system is overactive and it starts attacking and destroying its own healthy tissues and organs including the spleen.
Other factors that can contribute to spleen problems include:
- Spleen problems can also occur through injury such as accidents which breaks the spleen.
- Parasitic infections
- Cancers that can spread in your body
- Syphilis
Symptoms of Spleen problems
In many cases, an enlarged spleen may not show signs and symptoms. But if it does, you feel tired and bleed easily. You will also feel pain in your upper left region of the abdomen and the pain can spread to the shoulders.
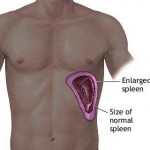
Figure 6 – Enlarged Spleen/ Size of Normal Spleen
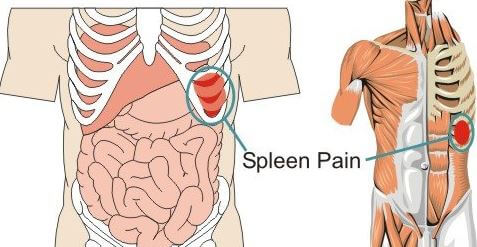
Figure 7 – Spleen Pain
Diagnosis
A number of tests can be done to diagnose the underlying causes of an enlarged spleen. These tests include:
Physical test
In this test, your doctor can press the belly below your left rib cage to feel the enlarged spleen. Your doctor can also check for other signs and symptoms that cause an enlarged spleen.
Biopsy
Your doctor can conduct a biopsy on your bone marrow. In biopsy, the doctor inserts a needle into a big bone such as pelvic and extracts a sample of your bone marrow. The sample is then analyzed to determine the cause of splenomegaly.
Ultrasound
Your doctor puts a probe on your belly, which releases high frequency sound waves that creates images as they are reflected by the spleen.
Magnetic resonance imaging
In this scan test, magnetic waves produce detailed images of your abdomen, which can reveal problems with your spleen.
Computed tomography scan (CT)
In this scan test, your doctor injects a contract dye into your veins to help enhance the images to be taken. The CT scanner takes several x-rays of your abdomen. Your doctor uses the computer to produce detailed images of your abdomen from those x-rays.
Treatment
Normally, treatment conditions focus on treating the underlying condition. A number of treatment options can be used such as:
Surgery
The entire spleen can be removed if it is seriously damaged. A surgery procedure called splenectomy is used.
In this procedure, your doctor can either make one large or several incisions on your abdomen and uses small surgical tools and camera to extract the spleen.
Once the spleen is removed, you are more prone to infections. After splenectomy, you will be vaccinated against particular bacteria and other pathogens. Vaccination for flu is normally given annually.
Removal of spleen may not affect your body from working. Other organs in your body such as lymph nodes and liver can perform the work done by the spleen.
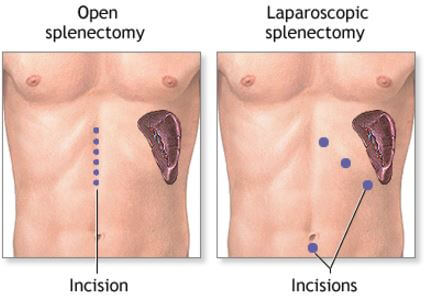
Image 8 – Splenectomy, Laparoscopic Splenectomy Incisions
Medications
Certain drugs can be given to treat various infections. For bacterial and viral infections, antibiotics and antiviral medications can be used to treat them respectively. Pain killer can also be used to relieve pain in your body.
Dental care
If the cause of spleen problem is Endocardiac, seek dental treatment to help prevent gum infections and other tooth diseases. You can also practice good oral hygiene by brushing your teeth regularly and floss once daily.
Reference List
- http://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/spleen
- function and disorders. Available at http://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/spleen
- Cirrhosis- Available at http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/172295.php
- Splenomegaly. Available at http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/206208-overview#a4
- Splenomegaly. Available at http://www.medicinenet.com/enlarged_spleen/article.htm
- http://www.livescience.com/44725-spleen.html
- Endocarditis. Available at http://www.webmd.boots.com/oral-health/guide/endocarditis-prevention
- Liver disease. Available at http://www.medicinenet.com/liver_disease/page3.htm