Skene Gland
What Is Skene Gland?
Skene gland is also called paraurethral gland, periurethral gland and lesser vestibular. This gland is found in female and is located in the vulva area, outside the vagina wall and near the urethra lower end.
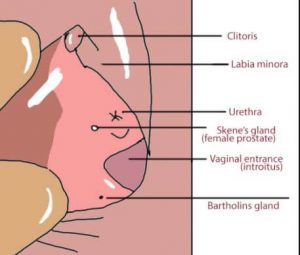
The gland may be part or near the G-spot and it drains into the urethra and urethra cavity.
Skene gland is encircled with tissues which can be part of the clitoris. Once a woman is sexually aroused, these tissues enlarge with blood. 4
This gland can be similar with the male prostate gland. The gland has many structures that are common with prostate gland such as secretory cells.
Functions
Skene gland is a capable of performing the following:
- Produce fluids to lubricate the opening of the urethra.
- The secreted fluids contain antimicrobial properties to protect the urinary tract against infection.
- It also secretes an ejaculate protein known as prostate-specific antigen which is found in males. Prostate-specific antigen is a type of protein produced by prostate epithelial cells
- whose function is to help to breakdown heavy proteins into polypeptides.
Disorders
Skene gland can also be infected just like many of the glands in a female body. The following disorders can affect the skene gland:
Skene duct cyst
Skene duct cyst is a condition characterized by swelling of the skene gland. The swelling occurs when the gland is obstructed which causes fluids to build up in the gland forming a cyst.
This gland can be infected by microbes such as bacteria, viruses and fungi.
The cyst can be painless but can also become severe and form an abscess. This condition affects adult women. The cysts are usually small in size but can develop into a lump near your vaginal region. This will make it difficult for you to walk or enjoy sex with your partner.
Symptoms
Female with Skene duct cyst can show any of the following symptoms:
A mass which is swollen and soft to touch can develop around opening of the vagina. This mass may not cause any pain in some women.
The cyst can grow and become large and block your urethra opening. The large cysts make it difficult and painful to urinate. Some women may develop fever as a result of abscess forming in the gland.
Those with abscess can experience pain and the gland can become swollen and red.
Another symptom is that an infected woman may have difficult in sitting and walking. Also the woman can not enjoy sex because it is very painful.
Diagnosis
Skene duct cyst can be confirmed through the following:
A physical examination
Your doctor examines your genital area to look for any swelling and redness near your vagina.
Fine needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy
The doctor can decide to analyze the fluid in the cyst. This is done through a procedure known as fine needle aspiration biopsy.
In this procedure, the doctor identifies the cyst and inserts the needle into it and drains out the fluid. The fluid is then taken to laboratory for analysis to determine the type of infection.
Mass biopsy
In mass biopsy, the doctor extracts the cyst and analyses it. This may help the doctor find out whether the cyst is cancerous or not. This test is recommended for women above the age of 40.
Treatment
When the cyst is small, there are no symptoms exhibited in those women. Therefore they may require no treatment for this disorder.
Managing this condition depends on the size of the cyst, its severity and whether the cyst is infected.
The following treatment methods can be used:
Antibiotic drugs
When the cyst infection is as a result of bacteria, antibiotic medication can be used treat it. Your doctor can prescribe antibiotic drugs such as penicillin.
Surgery
Surgery can be used when the cyst has become big. Your doctor cuts the cyst slightly to allow the buildup fluid to flow out. This reduces swelling and pain.
In some cases, the cyst may recur in other women. This can be treated through a surgical procedure called marsupialization. In this procedure, your doctor makes incision on the cyst and puts stitches on each side of the opening.
A tube called a catheter is put into the opening to help remove the fluid for several days.
Sitz bath therapy
Sitz bath therapy can also be used to relieve pain and swelling in the genital area. You can have a sitz bath in a bathtub or with a customized sitz bath that can fit in your bathroom.
Before using the sitz bath, clean properly and fill it with warm water. This water should be enough to cover your perineum. Immerse yourself into the water for a maximum of 20 minutes.
Once you are done, dry yourself with a clean towel and clean the sitz bath for the next bath. This should continue for at least four days to help break the cyst and drain the fluid.
Sitz bath may not work well for some women, so seek advice from your health professional before using this therapy.
Tips to Prevent
Side effects arising from skene’s duct cyst can be managed when you follow the following tips:
- Use condom each time you engage in sex
- Drink a lot of water to help flush out toxic substances in your body
- Clean yourself and clothing regularly to prevent microbes from invading your body.
- Go for regular screening and examination of your genital area to help detect and treat any problem there.
Skenitis
Skenitis is a condition that causes inflammation in your skene’s gland. This condition can manifest the following signs and symptoms:
- Your urinary tract can be infected.
- Feeling pain at the opening area of the urethra
- The area around the urethral opening can be tender to touch.
- In some case, pus may come out of your skene’s gland.
- The gland can also become red and swollen
Skenitis can be managed through antibiotic medications to treat bacterial infection. In case antibiotic are ineffective, surgery and other therapies such as sitz bath can also be used in treating this condition.
Reference List
- Skenitis. Available at http://andrewsiegelmd.com/files/documents/Skenitis.pdf
- Skene’s duct cyst. Available at http://www.dovemed.com/diseases-conditions/skenes-duct-cyst/
- Skenitis. Available at http://en.medicalmeds.eu/index-1880.htm
- Skene’s duct cyst. Available at http://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/gynecology-and-obstetrics/benign-gynecologic-lesions/skene-duct-cyst
- Sitz bath. Available at http://www.healthline.com/health/sitz-bath#overview1