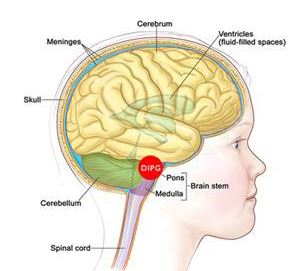
DIPG Tumor
What is DIPG Tumor?
DIPG is an acronym of ‘Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Gliomas’. DIPG is a type of brain tumor located at the base of the brain and highly aggressive in nature. Glial tissue present in the brain for providing protection and support to overall brain structure. DIPG tumor develops in the Glial tissues and infiltrates brainstem. The brainstem is the terminal end of the brain and controls several vital physiological functioning, which includes heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing1.
Prevalence
DIPG tumor is considered as a childhood tumor and almost 10 percent of central nervous system related childhood tumors are estimated as DIPG tumor. In the United States, approximately 300 children detected with DIPG tumor in every year. The onset of this tumor can occur at any age of childhood, but mostly 5 to 9 years old children have a greater affinity towards this tumor incidence. Both boys and girls have an equal potential risk to develop a DIPG tumor. However, the risk of the progression of this tumor in adult age is negligible1,2.
Symptoms
The DIPG growth rate is very fast and rapid before it can be diagnosed. The symptoms can start as early as three weeks after the development of the DIPG tumor and it may extend up to three months before the diagnosis start. The included symptoms are:
- Uncontrolled eye movement
- Hysterical facial expression
- Uninhibited chewing, swallowing and speech ability
- Upper and lower limbs weakness
- Walking and coordination problem2,3
Causes
The cause of development of the DIPG tumor is unknown. Yet now no evidence available to establish that DIPG is resultant of inherited disorder, as no responsible gene is identified that an affected child inherits from his/her parents.
No evidence found against environmental factors like smoke, radiation or chemical exposure responsible for DIPG onset.
Recent research supported that brain development has a significant role in DIPG tumor progression. According to this research, particular brain cells develop during the fastest brain developmental stage, which is considered as age between 5 to 10 years of childhood. This concept can also explain why DIPG tumor is not developing at adult age.
The genetic and epigenetic mutations involve in DIPG tumor development is detected in an ongoing research. But additional research requires continuing for establishing the mechanism of this mutation involve in DIPG tumor development. In addition, scientists also trying to know about what type of mutation and the reasons behind such involve mutations cause DIPG tumor development3,4.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of the DIPG tumor is essential for treatment commencement, however, the detection is difficult due to the location of the tumor. After a complete physical examination, doctors mostly prefer to utilize imagining diagnostic tools to detect the DIPG tumor diagnosis. The following are the DIPG tumor diagnosis:
CT scan can provide both horizontal and vertical cross- sectional images of the location.
MRI can provide detail anatomical reports, which is important to distinguish between tumor and normal tissue growth.
MRS (magnetic resonance spectroscopy) this diagnostic tool is additional conduction along with MRI to detect the nature of tumor means it can assist to detect the tumor is a glial or astrocytic tumor or a neuronal tumor.
Biopsy – The typical biopsy test is not performed to detect DIPG tumor because it increases the risk of damaging the underlying neurological structure. Therefore the classic biopsy method is not a helpful option for DIPG detection. But medical advancement can provide safe biopsy for DIPG tumor detection conducted under a specialized pediatric neuro-surgeon2,4,5.
Treatment
The treatment option may change depending on the patient condition and doctors decision. The following treatment options may not be beneficial for the affected patient, because of the complexity of the DIPG tumor:
Surgery
The surgical option may not be useful for most of the DIPG tumor. Because the chance of damaging the underlying nerve tissue is higher and that even cause a fatal outcome. The nature of the DIPG tumor is not a solid mass, therefore complete removal of the tumor through the surgical incision is not possible. Some of the cancerous growth remain and that continue to re-growth of the DIPG tumor.
Radiation
Radiation therapy provides maximum treatment benefits. It has been noticed that radiation can provide shrinkage of the DIPG tumor in almost 70 percent of the affected children. The resultant of this cause symptomatic relief associated with DIPG tumor.
However, radiation therapy does not provide long-term treatment benefits and unable to increase survival period. Because the shrinkage of the tumor in temporary and after a short time interval the DIPG tumor size again redevelop. Utilizing proton radiation therapy also unable to provide additional benefits in DIPG tumor treatment.
Researchers also trying to search added benefits in combination therapy of radiation with radiosensitizers. But no promising result yet obtain from the research result.
Chemotherapy
Almost 250 clinical trials completed over a past 30 years for detection of the efficacy of several chemotherapeutic agents. Utilizing both single and combination therapy in these clinical trials did not show the effective result to cure or improve the survival rate of the DIPG patients. But clinical researchers continue their research to find out new chemotherapeutic agents for treating DIPG patients in future2,5,6.
Prognosis
The prognosis of the DIPG tumors is very poor. Medical advancement unable to give any satisfactory result in DIPG treatment or survival rate of the affected individuals. The average life span of the affected children with DIPG tumors is nine months. Yet now only 10 percent of the DIPG affected children survive for two years after their diagnosis and only one percent of affected children have survival rate extended up to 5 years2.
References
- DIPG tumors Fact. https://www.defeatdipg.org/dipg-facts/overview/what-causes-dipg/
- Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma (DIPG). http://www.danafarberbostonchildrens.org/conditions/brain-tumor/diffuse-pontine-glioma.aspx
- DIPG tumors Fact. https://www.stbaldricks.org/blog/post/what-i-learned-from-my-daughters-deadly-brain-tumor-diagnosis
- https://www.defeatdipg.org/dipg-facts/overview/what-is-the-treatment-for-dipg/
- DIPG tumors Fact. https://www.defeatdipg.org/dipg-facts/overview/what-is-the-prognosis-for-a-child-diagnosed-with-dipg/