Eczema Herpeticum
What is Eczema?
Eczema is a skin condition characterized by a rash of the affected part of the skin, leading to red, dry, irritated and itchy skin patches. In general, eczema is related to atopic dermatitis, an allergic reaction of the skin to an allergen which comes into contact with the human skin.
Eczema is characterized by periods of progression and remission, were no signs at all can be visualized. However, at another time the eczema of the skin can become aggravated and the signs and symptoms get worse, commonly referred to as a flare – up.
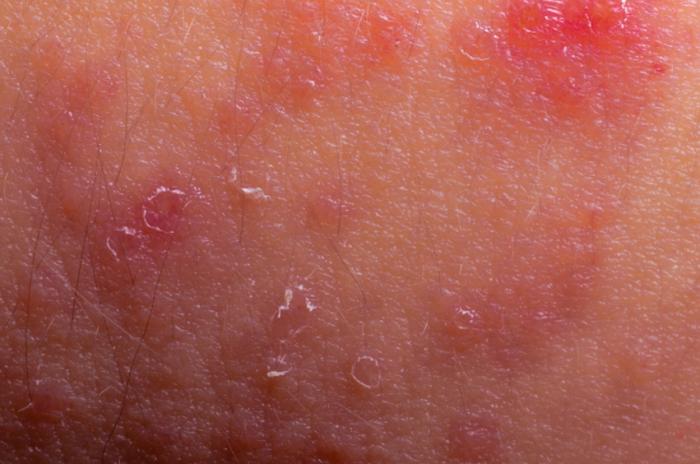
Eczema is usually triggered by a specific allergen so knowing what is causing eczema or what is making it worse is very important. Once the specific allergen is determined, a person should avoid these possible eczema triggers. Each person is unique, meaning that the eczema triggers vary from one person to the other. Common eczema triggers include:
- Allergens,
- Fragrances,
- Detergents,
- Certain foods,
- Stress, etc.
Eczema is not a serious medical condition even though it can become quite uncomfortable sometimes. Eczema flare – ups besides being bothersome cause no long – term complications. (1)
What is Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV)?
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) is a viral infection causing herpes. Herpes can affect any part of the human body. There are two types of HSV
- HSV 1 or oral herpes which is known to cause sores and blisters around the oral cavity and face,
- HSV 2 or genital herpes which is known to cause sores and blisters around the genital area.
This type of virus is contagious and can easily spread from one person to the other through direct contact or by sharing personal items. A person is more likely to transmit the virus to others when sores and blisters are present, even though the HSV can spread to others and when there are no signs and symptoms at all. HSV can affect anyone, regardless of a person’s age. If you are exposed to the infection, then you have a great possibility of getting infected.
Once infected with HSV, regardless if it is type 1 or type 2 of HSV, the infection has no cure, and the virus remains latent in the human body for life. In certain occasions, mostly when the immune system becomes weak, as well as in stressful situations the HSV becomes activated causing sores and blisters again around the mouth or around the genital area. In HSV outbreaks, antiviral medications such as topical or oral Acyclovir will help reduce the severity of the outbreak and prevent it from reoccurring in the future. But, this does not prevent the virus from spreading to other people. (2)
What is Eczema Herpeticum?
As mentioned everyone can get infected with HSV. However, in persons with a healthy immune system, the virus does not cause serious problems. However, if a person who already has eczema gets infected with HSV, they may develop eczema herpeticum.
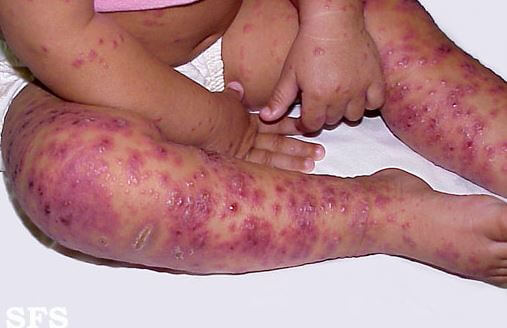
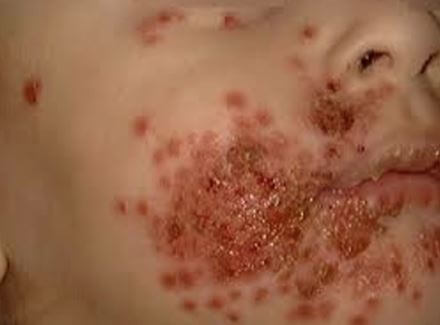
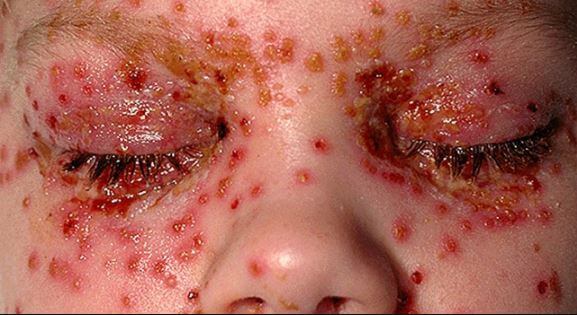
Eczema herpeticum is a rare complication, but a serious one. It occurs when a person who already has skin eczema comes in contact with sores and blisters caused by HSV, regardless if it’s type 1 or type 2 of HSV. It will take about 5 to 10 days before the signs and symptoms of eczema herpeticum become noticeable after being exposed to HSV. This type of eczema usually occurs in the head, neck or even trunk. Common signs and symptoms of eczema herpeticum are:
- Skin rash accompanied by blisters. Blisters may cover a large area of the skin, usually appearing in clusters. They may also become very painful, itchy, and even become filled with pus, bleed or break open.
- Swollen lymph nodes around the affected area of the skin,
- High fever,
- Chills,
- Fatigue,
- Filling ill, etc.
Eczema herpeticum is a serious medical condition which can lead to various complications. For this reason, proper diagnosis and treatment is needed. In rare cases, eczema herpeticum can even lead to death. Possible complications which can develop from eczema herpeticum include:
- Scarring of the skin from blisters,
- Blindness if the infection affects the cornea of the eye, commonly referred to as herpetic keratitis,
- Multiple organ failures,
- Death if the virus spreads to the human brain, lungs or liver.
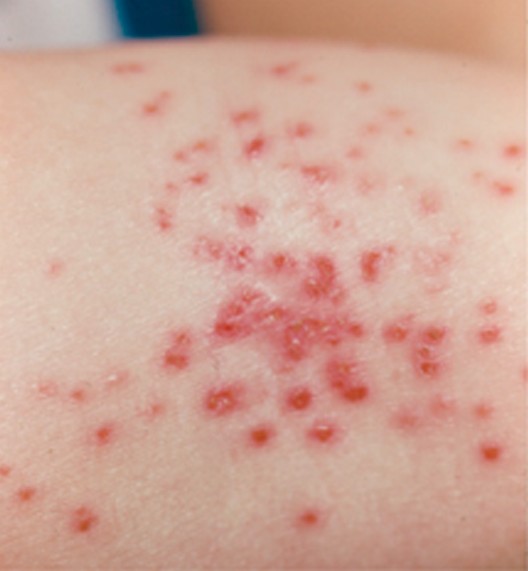
Eczema herpeticum
Certain people have an increased risk of developing eczema herpeticum, especially those who are dealing with chronic skin conditions like seborrheic dermatitis, contact dermatitis or who have had a skin burn recently.
Eczema herpeticum is more common among children and young adults. However, this serious medical condition can affect anyone with a vulnerable immune system. (3, 4, 5)
How is Eczema Herpeticum Treated?
Eczema herpeticum, as mentioned is a serious medical condition which requires immediate medical treatment with antivirals, as it can even lead to death if multiple organ failures develop and if the virus reaches vital organs such as the brain, the lungs or the liver. Often eczema herpeticum treatment requires hospitalization. (3, 4, 5)
How to Prevent Eczema Herpeticum?
The best way to prevent eczema herpeticum is to avoid any contact with a person who has sores and blisters caused by an HSV infection. Sharing the same eating utensils or personal hygiene items is also forbidden. This is especially important for children, young adults and all those persons who have a skin problem or a vulnerable immune system, as they have an increased risk of developing this serious medical condition.
Persons who have problems with eczema needs to learn the triggers and how to avoid them, minimizing this way the possibility of getting eczema herpeticum in the first place.
The following tips might help heal eczema faster, and preventing eczema herpeticum from developing
- Know the triggers which make your eczema worse,
- Use the medications prescribed by your doctor correctly for the treatment of your eczema,
- Keep a track of your eczema signs and symptoms and recognize on time any change or worsening of your symptoms,
- Moisturize your skin daily, as needed
- Avoid any contact with a person who has sores and blisters caused by HSV,
- Avoid sexual contact with people who might have genital HSV. Ask them to get tested for sexually transmitted diseases
- Practice safe sex by using condoms every time.
Consult a medical professional immediately after you notice any skin rash, sores, and blisters, or worsening of your eczema symptoms. Diagnosing and treating eczema herpeticum on time can prevent serious complications. (3, 4, 5)
Pictures
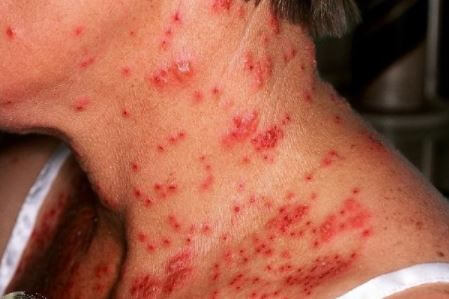
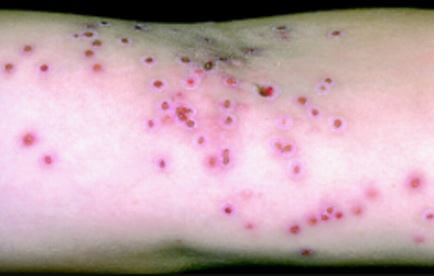
REFERENCE:
- Atopic eczema http://www.nhs.uk/conditions/Eczema-(atopic)/Pages/Introduction.aspx
- Herpes simplex virus, Retrieved from: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs400/en/
- Eczema herpeticum http://www.bad.org.uk/shared/get-file.ashx?id=197&itemtype=document
- http://www.dermnetz.org/topics/eczema-herpeticum/
- Eczema herpeticum: A dermatologic Emergency http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/443521
