Pyelonephritis
What is Pyelonephritis?
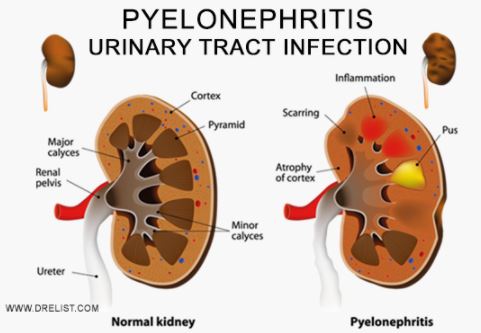
Pyelonephritis is a condition that causes the kidney tissue to be inflamed as well as the renal pelvis and the calyces. It is usually as a result of a bacterial infection that spreads in the urinary tract or travels via the bloodstream to kidneys. This condition makes the kidney to swell and can damage them permanently.
Pyelonephritis can even be fatal. When persistent attacks happen or a repeated, the disorder is referred to as a chronic Pyelonephritis. This chronic disease is very rare but mostly occurs to kids and individuals suffering urinary obstructions. 1, 2, 3
Once treated early, any kidney infection does not present serious harm, but one will definitely feel unwell. Once any kidney infection is not taken care of early, it can permanently damage the kidney. The signs of an infection in the kidney will be evident within the first few hours. One will start feeling sickly, shivery, and experience pain on the side or back.
Symptoms of Pyelonephritis
Acute Symptoms
Most of the patients suffering acute pyelonephritis will depict the below signs:
- Fever: this can at times not be present, but it is not uncommon for the temperatures to go beyond 1030F
- Vomiting and/or nausea: these will vary in intensity and frequency, from lacking to severe. Anorexia is very common for the individuals suffering from acute pyelonephritis.
Hemorrhagic cystitis or gross hematuria is common for many young women with this condition and uncommon in the males. The symptoms of this disease will normally show over a few hours or in the course of the day. If a patient is a child, elderly or male and has had the symptoms for 7 days for more, the infection will be deemed complicated till confirmed otherwise.
For the children who are 2 years and below, the major signs of any urinary tract infection will be:
- Vomiting
- Failure to grow
- Fever
- Troublefeeding
The elderly individuals may show symptoms of pyelonephritis, or may portray the below issuers:
- General deterioration
- Fever
- Change in the mental status
- Decompensating of another organ or body system
The symptoms and signs of pyelonephritis usually develop fast after some hours. It can make one to have pain when passing urine as well as some abdominal pains radiating along the flank to the back side. This is usually linked to vomiting. There could also be some blood present in the urine. 1,2
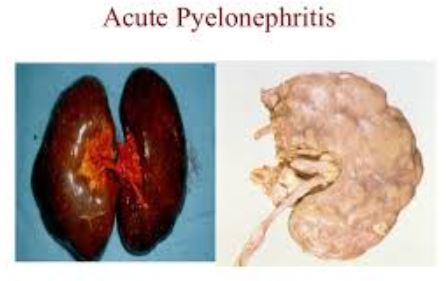
Acute Pyelonephritis
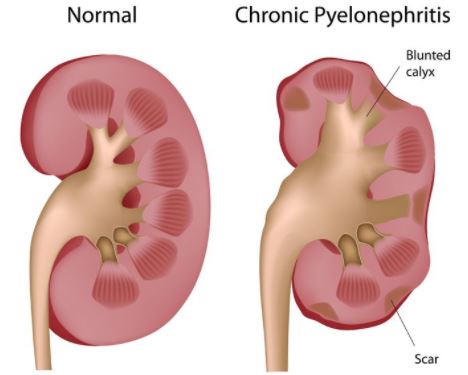
Chronic Pyelonephritis
Diagnosis of Pyelonephritis
For the outpatient circumstance, pyelonephritis is normally suggested by the history of the patient and he physical exams and is reinforced using the urinalysis results. The specimens of urine can be collected using the below methods: 2
- Suprapubic needle aspiration
- Urethral catheterization
- Clean catch
The urinalysis process can entail the following:
- Examination for microscopic and gross hematuria and proteinuria
- The nitrite production test that aids in screening for bacteria
- Dipstick Leukocyte esterase test that aids n screening for pyuria
The urine culture is shown in all patients with pyelonephritis, either treated in outpatient or inpatient setting, due to the possibility of resistance to antibiotics.
A few of the imaging studies used to assess acute pyelonephritis include:
Computed tomography scanning
This is used in identifying changes in the renal parenchymal perfusion, changes in the perinephric fluid, excretion, as well as nonrenalillness; inflammatory masses, obstruction, hemorrhage and gas forming infections.
Ultrasonography
This is used for screening for any urinary obstructions in kids suffering febrile diseases and examining patients for any renal abscesses, stones and acute bacterial nephritis.
MR and CT urography
This is used to evaluate hematuria
Scintigraphy
Aids in detecting central renal abnormalities
The below discussed tests will aid in diagnosing pyelonephritis:
Radioactive imaging
The dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) test can be used when the physician suspects any scaring due to pyelonephritis. This method is an imaging technique that aids in tracking an injection of radioactive substances. The doctor will inject the material in a vein in the patient’s arm. This material will then travel to kidneys. The images taken like radioactive substance pass via kidneys and will show the scarred or infected areas.
Urine tests
This test helps the medical practitioner to check for tenderness in the patient’s abdomen, fever and other signs. Once a kidney infection is suspected, a urine test will be ordered. This aids in checking for pus, bacteria, blood and concentration in urine.
Imaging tests
The physician can also do an ultrasound or an x-ray to search for tumors, cysts and other urinary tract obstructions. For the individuals who are unable to respond to treatment in 72 hours, a CT scan can be ordered. This test will also help show any obstructions in the urinary channel.
Treatment of Pyelonephritis
Different treatment approaches may be applied by a doctor to treat pyenonephritis. These include:
Antibiotics
The very first strategy for dealing with acute pyelonephritis is antibiotics. Nevertheless, the kind of antibiotic to be used by the doctor is dependent on if or not a bacteria has been identified. If there are no particular bacteria seen, a wide spectrum antibiotic will be administered.
Even though the drugs can treat the infection in a matter of two or three days, the drugs ought to be ingested for the whole prescription period, normally 10 or 14 days. Even when one is feeling better, they must take the entire prescription of the drug. The alternatives for the antibiotics are:2
- Ampicillin
- Cotrimoxazole
- Ciprofloxacin
- Levofloxacin
Surgery
Recurring kidney diseases can originate from a prevailing medical issue. In such cases, surgery can be needed to get rid of any kind of obstructions or to mend any structural issues in kidneys. Surgery can also be essential in draining any abscess not responding to the antibiotics. In instances of extreme infection, a nephrectomy would be necessary. During this procedure, the surgeon will get rid of a fragment of the kidney.
Hospital Admittance
There are cases whereby drug therapy is not effective. For the severe cases of kidney infections, the doctor can admit the patient to the hospital. The period of time one spends in the hospital is dependent on the severity of the condition as well as how well the patient responds to treatment. The treatment procedures can entail antibiotics and intravenous hydration for between 24 and 48 hours. During the stay at the hospital, the doctor will screen the urine and blood to track he disease.
Reference List
- What is kidney (renal infection) Pyelonephritis? https://www.urologyhealth.org/urologic-conditions/kidney-(renal)-infection-pyelonephritis
- Pyelonephritis. http://www.healthline.com/health/pyelonephritis#overview1
- Acute Pyelonephritis. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/245559-overview
- Kidney infection. http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Kidney-infection/Pages/Introduction.aspx