Lingual Tonsil
What Is Lingual Tonsil?
Lingual Tonsil is located in your oral opening and comprise mainly of lymphoid tissue. Tonsils protect the body against bacterial and viral infection they block microbes such as bacteria, viruses and fungi from entering your body through the oral way.
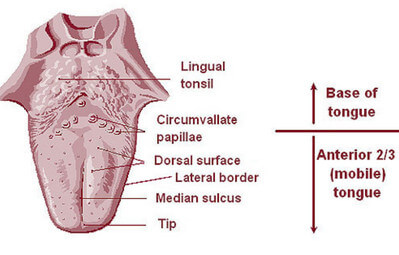
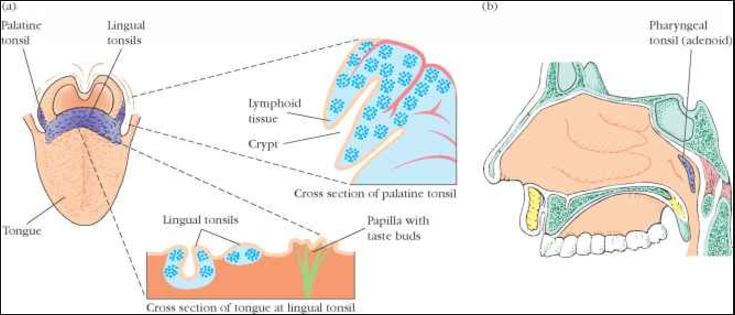
Lingual tonsils are situated near the rear end of your tongue, usually between vallecula layer and circumvallate papillae .
They form part of the lymphoid tissue and appear as small crypts and folds.
Lingual tonsils enlarge as soon as you are born until 7 years of age and start to reduce in size as you grow older.
Functions
Lingual tonsils main function is to cushion us against infections from upper respiratory system.
Features
Lingual tonsil is covered by epithelium. It also has tonsillar crypts which appear after you are born. These crypts are not deep and appear less branched than those in palatine tonsils.
Other features of Lingual tonsils include: adipose tissue, lymphoid follicles, skeletal muscles and mucous salivary glands.
Lingual Tonsillitis
In some cases, your lingual tonsils can become inflamed, a condition known as Lingual Tonsillitis.
Causes
Lingual Tonsillitis can be caused by the following:
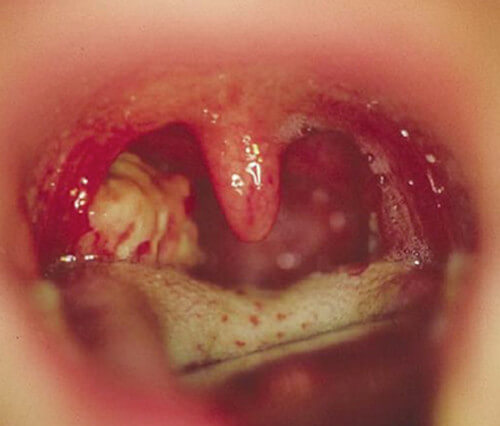
Fig. Inflammation of lingual tonsils
Infections
Bacteria and viruses are the main cause of inflammation in the lingual tonsils. Usually microorganisms enter your body through the nose and mouth.
They can find a breeding ground around lingual tonsils and reproduces to increase their populations. They then start to attack your lingual tonsils causing it to swell and become inflamed.
Lingual tonsillitis can also occur due to infections in the respiratory system4. Viruses are the main cause of infections in the respiratory tract, although bacteria can also cause it.
These infections can affect the upper and lower respiratory tract. The upper respiratory consist of throat, nose and sinuses while the lower has lungs and airways.
Upper respiratory infections affect children more than adults. This is because the immune system of children is weak to defend them against infections.
Transmission of respiratory infection
Respiratory infection can be transmitted in several ways. The infection can spread through sneezing or coughing.
When a person has cold, small fluid drops may contain a virus which is released into the air every time you sneeze.
When other people inhale this air, they may become infected.
Infections can also be transmitted indirectly. For instance, a person with cold can touch his/her nose or eyes prior to touching an object or surface.
When other people touch the same object or surface, the virus is transmitted to them and they get infected.
Poor dental care
Failing to adhere to proper oral and dental hygiene can cause infections that spread to lingual tonsils.
People who do not brush their teeth regularly attract bacteria in their teeth which cause gum infections. These bacteria can reach the base of your tongue and cause inflammation.
Poor dental care also involves failing to go for dental checkup. Dental checkup sessions are vital because the dentist can identify dental problems and help you manage them in the early stages.
If you do not visit a dentist regularly, you are more likely to develop serious dental problems that can also affect your tongue.
Other causes
Staying in a crowded environment- If you live in a congested place, you are more prone to respiratory infections which can cause Lingual tonsillitis.
Symptoms
An inflamed lingual tonsil is painful and makes it difficult for you to swallow food through the throat. The affected area is tender and swollen. You can also have fever and barely audible voice.
Lingual tonsils can become big and block airway preventing enough air from reaching your lungs and around the body.1,2
Diagnosis
Physical examination can be done to check for swellings in the lingual tonsils. Other tests such as a tissue biopsy can be used to determine the cause of the infections.
In tissue biopsy, your doctor scraps a sample of your lingual tonsil tissue and analyses to confirm bacterial or viral infections.
Treatment
Various treatment options are available to treat Lingual Tonsillitis. These treatments methods include:
Medications
If the cause of Lingual Tonsillitis is bacterial infection, you will be given antibiotics to treat it. For viral infections, your doctor will recommend antiviral drugs to cure it. Pain killer drugs can also be prescribed to help relieve pain.
Lingual Tonsillectomy
This procedure is used to remove the enlarged lingual tonsil to open the airway at the back of your tongue. Before the procedure, you will be given an oral antiseptic to wash your throat to prevent infections. Avoid use of aspirin before and after surgery to prevent bleeding.
In this procedure, you will be put under a general anesthesia so that you do not feel any pain during surgery. Your doctor pulls out your tongue with the lingual tonsil held tightly. The doctor uses a laser to remove lingual tonsil in order to reduce bleeding.
Complications
Lingual Tonsillectomy can cause undesirable side effects such as
Damage to the tooth
If you have a loose or decayed tooth, the tooth may be damaged during surgery.
Nerve damage
Nerves in the tongue can also be injured during this procedure. Damaged nerves can cause numbness in the tongue as well make it difficult for you to swallow food.
Pain
After surgery pain is so severe for two days and disappears. This pain reappears after 4 – 6 days and spreads to your ears. Pain can be relieved through pain killer medications.
Halitosis
After surgery, a layer can develop behind your throat and cause bad breath. You will be given antibiotics to treat halitosis and prevent infections after surgery.
Home Remedies
You can use the following homemade solution to treat Lingual tonsillitis:
Saline solution
You can also use salt solution to reduce inflammation in the lingual tonsils. This solution is simple to prepare; add salt to lukewarm water and rinse your throat with it.
Stop smoking and drinking alcohol because they may cause infections in the upper respiratory system.
Take good care of your teeth by brushing daily as well as visit the dentist regularly.
Avoid eating food which is hot, acidic and rough because it can worsen the pain.2
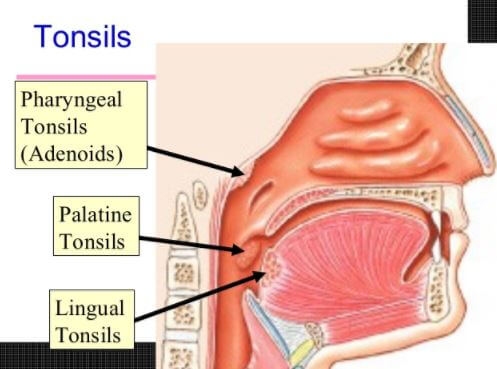
Pictures
Location & pictures of lingual tonsil.
Reference List
- Lingual tonsils. Available at http://healthfixit.com/lingual-tonsils/
- Lingual Tonsillitis. Available at http://www.tandurust.com/infections/lingual-tonsillitis-acute-and-chronic.html
- Lingual tonsillectomy. Available at http://www.sleep-doctor.com/surgical-treatment-overview/tongue-region-procedures/lingual-tonsillectomy/
- Respiratory tract infections. Available at http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Respiratory-tract-infection/Pages/Introduction.aspx
