Torus Palatinus
What Is Torus Palatinus?
Torus palatinus are bony growths on the palate or roof of your mouth. The growths are non-cancerous and therefore not a threat to your life. These growths are solid when you touch them and cannot be moved easily with your finger. 2
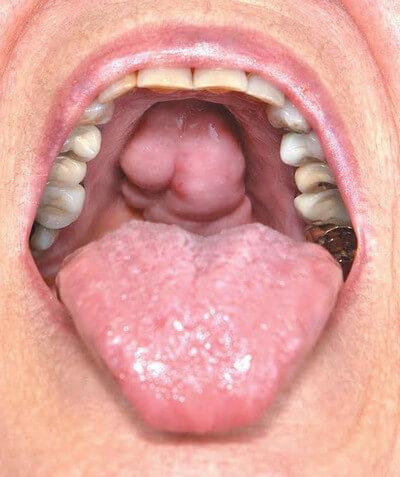
Medical reports show that torus palatinus affects more women than men. These growths can begin early in adulthood and decrease in size as you grow older due to bones being re-absorbed. These growths can also develop in infants and children due to the problem in the cleft palate. Congenital defects especially in the upper palate can also cause these growths in babies and children.
Torus palatinus can appear in either regular or irregular shape. Regular shapes of this growth include lobular or nodular.
Causes
Several factors can cause torus palatinus. They include:
Genetic factors
Scientists have found that genetics play a role in forming torus palatinus. Parents with torus palatinus are more likely to pass a copy of the defective gene to their offspring. In case, only one parent has torus palatinus, there is a low chance of passing the mutated gene to the child.
Injury
Injury to the bones of your oral cavity can also cause torus palatinus. Injury can be in form of accidents like falling from a tree or car accidents which directly involve bones in the oral cavity.
Bruxation and clenching
Torus palatinus can arise from certain habits of your teeth. Your teeth can grind together when your teeth are in motion or static. These can cause wear and tear of your teeth and also affect your chewing muscles.
Calcium and vitamin deficiency
Calcium and vitamins are important in your body. Your body needs calcium to form strong teeth and bones. Vitamins especially vitamin D helps your body to easily absorb calcium and use it to perform its function.
Once your body gets inadequate calcium, you are more prone to many diseases as well as develop weak bones and muscles. Low calcium in the body is attributed to your body’s natural processes. Normally, your body keeps calcium in the bones. When you grow older, your bones start to emaciate and become less thick.
Low calcium in the body can also occur in patients with hyperparathyroidism. It is a condition where thyroid gland produces little amounts of thyroid hormones. Thyroid hormone regulates the level of calcium in your body. When thyroid hormones are little in your body, calcium levels available for use in the body also drops.
Calcium deficiency can also arise from your body inability to absorb vital nutrients and minerals. Excess potassium in your body can destroy calcium by burning it hence reducing its quantity. Low vitamin D in your body prevents absorption of calcium in your body.
Medication
Drugs used to treat seizures or muscle spasms can cause torus palatinus.
Symptoms
The main symptom of torus palatinus is having difficult in eating and drinking. In some cases, torus palatinus can form a growth that looks like a tumor.
Diagnosis
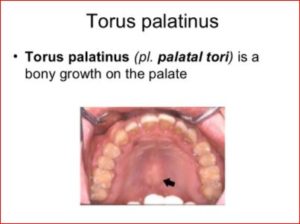
Torus palatinus can be diagnosed through clinical examinations. Your doctor can use dental x-ray test to confirm this condition. Dental X-ray involves use of X-rays to provide detailed pictures of bones and teeth. These pictures can assist the doctor detect problems with your mouth, teeth and jaws.
Various dental X-rays exist and your doctor can choose which one to use depending on the location of the problem in your mouth, teeth and jaw. For torus palatinus, your doctor will use Occlusal X-rays to check the roof or floor of your mouth. Occlusal X-rays helps the doctor determine growths, cleft in the roof of the mouth and fractures in the jaw.
Preparation for the test
Before undergoing dental X-ray test, inform your doctor if you are expectant. Although dental X-rays are conducted in the mouth, expectant women are not allowed for the test.
This is because the test emits some radiation that can be transmitted around the body and affect the fetus. For pregnant women, your doctor can advise them to come back after they have delivered the baby.
Apart from pregnant patients, you do not need to prepare for anything else.
Procedure
Your technician covers your body with a lead apron to protect you from x-ray radiations. The x-ray takes pictures of your teeth, jaws and bone.
Alternatively, your doctor can use a digital radiography to carry out the test. In this method, an electric sensor is used to take detailed pictures of your teeth, jaws and bones. This method emits less radiation as compared with dental X-ray.
Other techniques can be used to determine bone abnormalities and soft tissue problems. These techniques include use of CT and MRI scan.
Treatment
People with torus palatinus are unaware if they have them. These bony growths are identified when you visit your health provider.
Your doctor may decide whether to treat the growth or not depending on the size of the growth. Small growths may not be treated if you they are not causing any problem.
Large torus palatinus can affect your oral hygiene, interfere with dentures and prevent prostheses to be placed in your teeth. These bony growths can also spread infections to the bone and palate in your mouth.
Large torus palatinus can be removed through surgery by specialized surgeon in maxillofacial procedures. In this procedure, the surgeon gives you general or local anesthesia to help minimize pain during the process.
Your surgeon ensures that the torus palatinus can be seen clearly by staining it. When the torus palatinus is visible, the surgeon cuts the area until the soft tissue is exposed and removes torus palatinus.
When this procedure is finished, some complications may arise. They include the area can become swollen as well as you can experience bleeding from the surgery site.
The area can be infected with bacterial and viral infections. Some people can react to anesthesia used during surgery.
The healing of the wound may vary from one individual to another. The wound can heal completely after 4 weeks.
When you notice a new growth or any form of growth, seek medical help to exclude the possibility of cancer of the mouth.
Reference List
- Torus Palatinus. Available at http://medmum.com/torus-palatinus/
- Torus palatinus. Available at http://healthool.com/torus-palatinus/
- Torus palatinus. Available at http://healthfixit.com/torus-palatinus/
- Calcium deficiency. Available at http://www.healthline.com/health/calcium-deficiency-disease#overview1
- Dental X-Rays. Available at http://www.webmd.com/oral-health/dental-x-rays#3
