Endosteum
What Is Endosteum?
Endosteum is a structure found on the inner surface of the bone. It is a membrane layer that coats the medullary cavity, bony trabeculae; the spongy part of the bone, inner walls of the compact bones and haversian canals.1
Endosteum has cells known as endosteal. Endosteal consists of many cells such as bone stem cells; which forms osteoclasts and osteoblasts cells. Osteoclasts cells help dissolve the bone while osteoblasts cells are responsible for forming bones in your body.
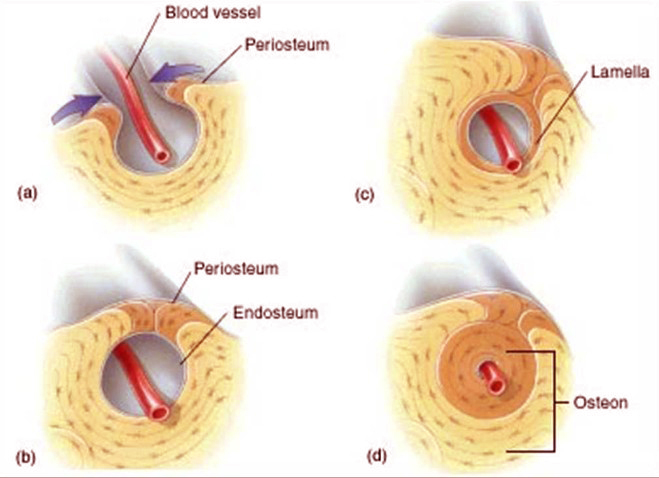
Endosteum also has few connective tissues fibers and blood vessels. These blood vessels transport nutrients to nourish the endosteum.
Types
Endosteum can be classified into three groups. They include:
Trabecular endosteum
It covers the bony trabeculae.
Osteonal endosteum
It coats osteonal canals.
Cortical endosteum
It detaches other structures from the bony marrow opening.
Purpose
Endosteum can perform various functions in your body such as
Remodeling bones
Our bones continue to be renewed after birth and into adulthood. Bone remodeling is a process of replacing old bones with new tissues. In this process, osteoclasts cells break down the old bones, a process known as bone resorption. Osteoblasts cells produce new bones to replace the old bones.
Repairs damaged bones
Endosteum can help repair fractures and damaged bones. Repairing broken bones or fractures takes four steps as discussed below:
Forming hematoma
When the blood vessels around your bones are damaged and bleed in the bones forming a hematoma or a blood clot at the site of injury. The damaged blood vessels deprive the cells of bones vital nutrients for growth and as result they die.
Generating the bone
Blood capillaries start to grow in the affected area of your bone. The phagocytic cells start to get rid of the dead cells at the site of injury. Osteoblasts and fibroblasts go in the affected area to help in restructuring the bone.
Fibroblasts cells manufacture collagen fibers that attach the ends of the broken bones. Osteoblasts form the spongy bone.
Forming callus
The tissue between the ends of a broken bone is known as fibrocartilaginous callus. Osteoblasts multiply and converts fibrocartilaginous callus into a bony callus. The broken ends of the bone can take nearly two months to be firmly attached together after injury.
Remodeling the bone
In remodeling stage, osteoclasts and osteoblasts remodels the bony callus and removes unwanted material on the bone and in the medullary cavity.
These cells add the compact bone to the bony callus to form a bone tissue that is similar to the original, normal bone. This process can take several months for the bone to heal completely.
Encourage growth of bones
Endosteum can allow bone to grow in width and thickness. It stimulates osteons in the cartilage bone to grow thick.
Abnormalities in Bone Remodeling
Problems in the bone remodeling can lead to life-threatening skeletal disorders. These disorders include:
Osteomalacia and rickets
Low levels of vitamin D in the body can lead to osteomalacia and rickets disorders. Rickets affects children while osteomalacia occurs in adults.
Normally people gets vitamin D by eating food rich in vitamins and exposure to the sun. Therefore consuming food without vitamin D and little or no exposure to sun can reduce Vitamin D in your body.
These disorders can cause pain in the bone and weaken muscles of the patients. They also elevate your vulnerability to fractures with or without any form of trauma. Some infants can experience convulsions.
Paget’s disease
Paget’s disease is a disorder that interferes with normal bone remodeling process. It occurs when osteoclasts cells become hyperactive which leads to irregular patterns of breaking the bones. As a result the osteoblasts respond by slowly forming new bones.
Bones affected by Paget’s disease are less dense, fragile and vulnerable to fractures.
The exact causes of Paget’s disease are unknown. However various risk factors have been identified which can cause this disease. They include
- Age– Paget’s disease can start at age 55. Those people above 55 years are at high risk of developing this disease.
- Genetics– Studies have shown that particular genes are responsible for this disease. Sequestrosome 1 gene on chromosome 5 can cause Paget’s disease.
- Infections– Viral infections can also trigger this disease in people who have a copy of the defective gene that cause Paget’s disease.
Paget’s disease can be treated with bisphosphonates. This drug can be taken orally or through injection. Examples of this drug include: Ibandronate, Zoledronic acid and Alendronate.
In severe cases, surgery is used to treat the affected bone. Surgery can replace damaged joints, lower pressure on the nerves and straighten a deformed bone.
Osteoporosis
This is a medical condition where bones are not dense and become more fragile. Osteoporosis weakens the bones and can lead to regular fractures in the bones.
Osteoporosis can occur in people due to the following:
- Eating food without calcium, which is responsible for healthy and stronger bones.
- Drinking too much alcohol
- Low levels of hormones in the body. In women little estrogen hormones especially during menopause or when ovaries are surgically removed can cause this disease. Men with low testosterone hormones are at a higher risk of getting osteoporosis.
- People with inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis are more likely to develop this disorder.
- Lack of exercise weakens your muscles and elevates your risk of developing osteoporosis.
- Hyperparathyroidism- This is a condition where parathyroid gland secretes excess parathyroid hormone in the body.
- This hormone is responsible for regulating the amount of calcium in the body by removing it in the bones. In case of too much production of parathyroid hormones in the body, excess calcium will be removed from the bones causing osteoporosis.
Managing Bone Disorders
Skeleton disorders mentioned above can be easily managed when you change your lifestyle. The following tips can help you maintain healthy and strong bones and muscles:
- Increase intake of food rich in vitamin D, vitamin C and calcium. You can eat foods such as fish, kales, Yogurt, milk. Expose yourself to the sun daily to get natural vitamin D. You can also get recommended supplements for calcium and vitamin D.
- Avoid drinking alcohol and quit smoking.
- Exercise regularly to strengthen your muscles
Skeletal disorders are best treated in a hospital. When you have fractures, seek medical attention for early treatment in order to avoid serious complications.
Reference List
- Endosteum. Available at http://healthfixit.com/thecal-sac/
- Endosteum. Available at http://byebyedoctor.com/endosteum/
- Physiology of Bone Formation, Remodeling, and Metabolism. Available at http://www.spinedragon.com/student_material/reading/2017_bone_formation_remodelling.pdf
- Osteoporosis. Available at http://www.medicinenet.com/osteoporosis/page10.htm
- Paget’s disease. Available at http://www.medicinenet.com/pagets_disease/page2.htm
- Osteomalacia and rickets. Available at http://www.netdoctor.co.uk/conditions/aches-and-pains/a2843/osteomalacia-and-rickets-vitamin-d-deficiency/
