Aneurysmal Bone Cyst
What Is Aneurysmal Bone Cyst?
Aneurysmal Bone Cyst is a cavity that forms in your bone that is filled with fluids. Bone cyst can affect any person, but it is more common in young adults and children2.
Bone cysts are of two types: Aneurysmal bone cyst and Unicameral bone cysts.
Aneurysmal bone cyst is uncommon form of bone cyst where your bone has blood1. This type of bone cyst can occur anywhere in your body, but it normally affects your spine, pelvic, upper arm and legs.
Children of age bracket 15 to 20 years are highly affected by aneurysmal bone cyst. There is a general notion that this type of bone cyst affects female more than men. People with aneurysmal bone cyst can still develop this condition even after treatment.
Aneurysmal bone cyst is non-cancerous lesion in your bone but grows rapidly. It can happen suddenly or as reaction to other tumors present in your body. Various studies has shown that patients with tumors especially chondroblastoma also developed aneurysmal bone cyst5.
Causes
Although the causes of this condition are unknown, medical studies are associating aneurysmal bone cyst with a defective gene known as ubiquitin specific peptidase 6 (USP6) on chromosome 17.
Symptoms
Symptoms associated with aneurysmal bone cyst include:
Patients feel pain and swelling in their bones. The pelvic, upper arm, spine can become stiff and reduce movement in the affected areas. The affected areas can feel warm when you touch.
Diagnosis
Aneurysmal bone cyst can be confirmed through the following diagnostic tests:
Biopsy
A doctor inserts a needle into your affected area such as spine, upper arm or pelvic and extracts some tissues or fluid. These tissues or fluids are taken to the laboratory and analyzed to determine the cause of this condition.
Imaging tests
The following imaging tests can be used by your doctor to assist in diagnosing this condition:
X-rays
This test is used to show clearly the images of your bones. The doctor studies the images to identify any abnormality in your bones.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
This test uses powerful magnetic fields to create detailed images of your bones, soft tissues and ligaments. During this test the patient is not exposed to any radiation.
Computed tomography scan (CT scan)
This test combines computerized applications and X-rays to produce images of the inner parts and organs of your body. The CT scan takes images of various section of your body.
For CT scan, your child may be required to do some preparations before the scan. As parents ask your doctor any preparation you can do for your child before the exam.
EOS Imaging System
This test is used to scan a patient while standing upright and produces 3 dimensional flat images of the body. This test enables a doctor to view clearly the lower limb and spine in a natural position.
Because of its little radiation, this test is suitable for children with conditions such as spinal problems that need regular imaging to check the progress of the disease.
The images taken by this imaging system will be examined by your doctor to help diagnose aneurysmal bone cyst.
Angiography
This is a type of X-ray test that checks circulation of blood in your blood vessels. It uses a fluoroscope and a dye to produce clear pictures of your blood vessels.
In this test, your doctor places a catheter into your blood vessels and directed to the exact area of study. Your doctor then injects a dye or a contrast material in your vein to enhance the images taken.
This test can help your doctor diagnose aneurysmal bone cyst. It can reveal problems in your blood vessels such as bulging of the vessel wall (aneurysms).
Treatment
Several treatment options are available to manage this condition. These treatments are as follows:
Bone transplanting
Bone transplanting or bone grafting is a procedure done surgically to correct your bones and joints problems. Bone transplanting can be done to heal a fracture in your bone. It can also be conducted to help a wound heal near an implanted device.
Bone grafts are of the two types and your doctor may decide to use any of them or an artificial one. These bone grafts are:
- An allograft – This graft is derived from a dead person body.
- An autograft – This type of bone graft is obtained from a bone in your body such as pelvic or hips.
The use of these forms of bone grafts depends on the nature of injury on your bones.
Preparation
Before bone grafting procedure, your doctor can carry out a physical exam of your bones as well as discuss your medical history. Your doctor will issue the rules and regulations you must adhere to before surgery to avoid any problem during the procedure. For children, parents should help prepare them for the procedure.
How it is conducted?
Once your doctor has selected the type of bone graft to use, you will be given general anesthesia. This is given to help you fall asleep so that you do not feel any pain during surgery.
Your doctor cuts the skin where the graft will be placed. The bone to be used is the shaped in order to fit in the pace. The graft is then held in pace on the bone by screws, pins or wires.
After securing the graft firmly in place, the doctor uses stitches and bandages to cover the wound.
Complications of bone graft
Bone grafting can also produce undesirable complications such as:
- You can feel pain in the grafted area
- The bone graft may be rejected by your skin.
- The area near the bone graft can become inflamed and swollen.
Intralesional curettage
In this procedure, your doctor administers general anesthesia so that you donot feel any pain during the procedure. Your doctor makes an incision in the affected area and scraps the bone and extracts the cysts.
Intraoperative adjuvants
This type of treatment involves use of several methods to remove a bone cyst. Your doctor can use chemicals, liquid nitrogen or burn the cysts with electric current.
Aneurysmal bone cyst can recur even after treatment. Going for regular medical screening and physical examination of your bones can help manage this condition. For children’s, parents should ensure they go through this medical checkup to help them grow properly.
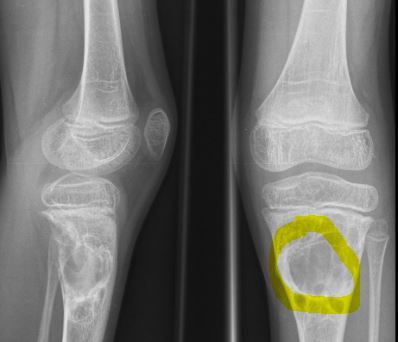
Pictures
Reference List
- Aneurysmal Bone Cyst. Available at http://www.chop.edu/conditions-diseases/aneurysmal-bone-cyst
- Bone cyst – Treatment. Available at http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Bone-cyst/Pages/Treatment.aspx
- Aneurysmal Bone Cyst. Available at http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1254784-overview
- Bone graft. Available at http://www.healthline.com/health/bone-graft#overview1
- Aneurysmal Bone Cyst (ABC). Available at http://www.dovemed.com/diseases-conditions/aneurysmal-bone-cyst-abc/
