Orbicularis Oculi
What Is Orbicularis Oculi?
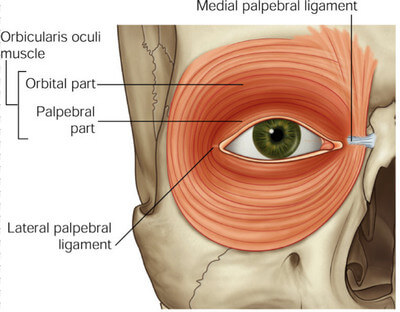
Orbicularis oculi muscle is generally a circular muscle located below your skin, around your eyes4. It has skeletal muscles and nerves from the face nerve.
The nasal part of the front bone and the frontal side of tendo oculi is where this muscle originates from. This muscle also arises from the anterior process of of the upper jaw.
Parts of Orbicularis Oculi
Orbicularis oculi muscle is divided into the following components:
Orbital
This part forms round fibers that enfold around your eyes and combine with the surrounding muscles on the orbit. Orbital part is thick and red in color and forms an elliptical structure on the side of palpebral commissure. Palpebral commissure is where the lower and upper eyelids that is near to the side angle combine.
Palpebral
This part of orbicularis oculi is skeletal and pale in color and starts from the splitting of tendo oculi and traverses both of the eyelids to mix sideways with eye. Palpebral muscle puts into side of palpebral ligament at the external corner of the eye. It is used to help your eyelids blink and wink. Palpebral is divided into the following:
Pretarsal muscles – They are found at the front part of the tarsus and it is connected with medial palpebral ligament.
Preseptal
These muscles are placed on top of orbital septum and originate from a deep head linked to medial palpebral ligament.
Lachrymal
This is a tiny, skeletal muscle found at the back of tendo oculi and lachrymal case. It splits into lower and upper slips after traversing the lachrymal case.
Functions of Orbicularis Oculi
Eye Closing & blinking
Orbicularis oculi assists in closing and blinking of your eye. This is achieved through the three parts of orbicularis oculi muscle. Palpebral muscle helps in closing the eyelid involuntary especially when a person is sleeping. This muscle works together with the check, forehead skin and temple to shut the eyelids.
During closing of the eyelid, your skin folds and spread out from the sideway angle of the eyelid. As you grow older, the folds on your forehead skin become permanent and forms wrinkles.
The orbital and palpebral muscle contracts and relaxes respectively to assist in reducing glaring. The lachrymal gland facilitates tears to flow over skin of the eye. The medial fibers help to remove tears from the eye and move them via the duct and lachrymal sac. The lachrymal sac muscles ensure that the tear channel is impermeable.
Orbicularis Oculi Problems
Orbicularis oculi muscle can become impaired and affect closing and blinking of your eyes. This impairment can arise from diseases or injury to the eye or facial muscles or nerves. Infact conditions that cause facial paralysis are connected to the impairment of orbicularis ocul muscles.
Facial paralysis occurs due to a damaged nerve and leads to loss of movement in the face. This paralysis can affect one or both sides of your face. It can last for a short time or a longer period depending on the cause of the paralysis. The following are some of the causes of facial paralysis:
Stroke
Stroke occurs when blood flow to your brain is disrupted which stops parts of your body that depend on affected brain cells from working. Stoke can be as a result of bleeding in the brain tissues, which is known as hemorrhagic. It can also occur when blood supply to the brain is lost, a condition known as ischemic stroke.
Different strokes affect your brain differently and depend on the part of your brain affected. Stroke that occurs on the right side of your head would weaken the left side of your body. This also relies on the location of the injury in your brain. In most cases, the right stroke can affect your face and lead to facial paralysis. Other parts of your body that can be affected by the right stoke include arm, leg or it can occur in these two and the face at the same time.
Stroke that occurs in the left side of the brain affects the right side of your body. It also affects your speech and understanding of things since it in the left side of your body where speech is located.
Stroke is a life- threatening condition that can cause death if not treated early. Ischemic stroke can be treated when the symptoms of stroke are detected early.
Stroke Triggering factors
- High blood pressure
- Too much fat in the body
- Smoking
- Diabetes, there is too much sugar in the body.
Signs and symptoms of stroke include the following
- People with stroke can have loss of vision in one eye or both. Confusion, difficulty in speaking is also reported in many cases of stroke. One part of your body becomes paralyzed or weak.
Bell’s palsy
This is condition in which one side of your face is paralyzed. It can occur as a result of damage to the nerve in your face that regulates facial muscles. This causes the affected side of your face to become flat and sometimes droop.
The causes of Bell’s palsy are not yet known. However, it is believed that this condition can result from a viral infection such as herpes virus. Paralysis can also occur when the facial muscles are damaged due to inflammation.
Other factors
- Presence of tumor on your neck or head
- Autoimmune diseases which attack and destroy your facial tissue
- Infection in your middle ear
- Face injury or fracture in your skull.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of facial paralysis starts with a physical exam. Your doctor can ask you to lift your eyebrows, close your eye and frown.
Other test that can be done include electromyography, which tries to determine the health of facial muscles and the nerves that regulate them. Imaging scan such as Magnetic resonance imaging can be used to identify abnormalities in the soft tissues of your face and eye. Blood tests can also be performed to confirm the cause of facial paralysis.1
Treatment
Managing facial paralysis depends on the underlying cause. For Bell’s palsy, the condition can go away without treatment. However, medications such as corticosteroid can help you recover from this condition. This medicine is effective when you take it immediately the symptoms starts.
Strengthening exercises can also help in relaxing your facial muscles and enable you recover faster. You can tighten and relax your facial muscles or massage your forehead, cheeks or lips with cream.
Facial paralysis caused by stroke can be treated by medications or stroke therapy. In stroke therapy, your doctor performs surgery to remove blood clot causing stroke. You can also receive medications to prevent stroke from spreading to your brain.
For other facial paralysis, surgery can be done to replace damaged muscles or nerves.5
Reference List
- Facial paralysis. http://www.healthline.com/health/facial-paralysis#treatment5
- http://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/orbicularis-oculi-muscle
- http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/834932-overview#a4
- Orbicularis oculi. http://www.knowyourbody.net/orbicularis-oculi.html
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003028.htm
