Urethral Stricture
What Is Urethral Stricture?
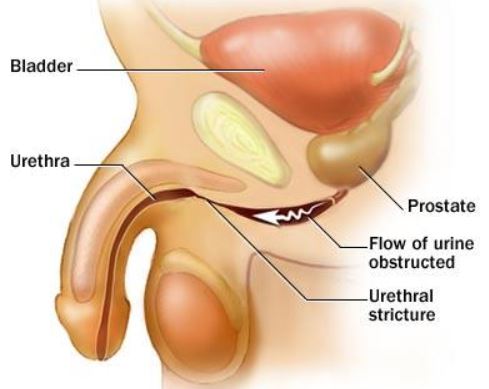
Urethra is a tube that moves urine to the bladder so that it is removed from the body. Urethral stricture is a condition where your urethra becomes narrow due to diseases, injury or infections. The narrowing of the urethra obstructs urine form being expelled out of the body which can lead to urinary tract infections and inflammation. Urethral stricture affects men more than women because males have a long urethra5.
Causes
Urethral stricture can be caused by numerous factors such as
Injury or damage
various injuries occurring on your pelvic can damage your urethra. For example you can fall from a tree or be involved in road accident can destroy your urethra.
Surgical operations which involve inserting medical instruments into the urethra can damage urethra tissues. For example an endoscope is normally inserted into the urethra to view your urethral structures.
Infections
Infections that occur in the urinary tract can cause your urethra to become inflamed and swell hence preventing urine from being drained out of your body. A number of infections can affect your urinary tract such as
Sexually transmitted infections
Infections that result from sexual intercourse can make your urethra to become inflamed. These infections include
Gonorrhea
This is a sexually transmitted infection caused by bacterium known as gonococcus. It is transmitted through having sex with an infected person. Gonorrhea can spread up to your urethra and constrict or narrow it forming a stricture.
Chlamydia
Chlamydia trachomatis bacterium triggers Chlamydia. The infections occur when you have sex with an infected person. Chlamydia normally affects the urethra that passes urine into the penis in men while in women it affects the cervix and the womb.
Cancer
Tumors that form close to the urethra can narrow it forming a stricture.
Enlarged prostate
The prostate gland is located between your penis and the bladder. It surrounds the urethra. The prostate gland can grow bigger and partly obstruct the urethra. The enlargement of the urethra is as a result of hormonal changes and it is not connected to cancer. Enlarged prostate affects mostly men and mostly occurs in older men of 75 years of age.
Use of catheter
A catheter is a tube inserted into the urethra to drain urine out of your body. A catheter can be used for a short time or a prolonged period depending on your condition. This tube can attract bacteria that cause infections that spread to the urethra and cause inflammation.
Symptoms
- Patients with urethral stricture can have trouble in urinating; they strain to urinate and sometimes it is painful. In some cases urine can leak without a patient knowledge and some patients report increased urge to urinate frequently. The stream of urine can occur slowly or suddenly with spraying of urine.
- Other signs and symptoms of urethral stricture include: In males, they can notice blood or discharge coming out from the penis. Some patients also complain of pain the lower abdomen and pelvic.
Diagnosis
Several exams and tests can be used to diagnose urethral stricture. They include
Physical exam
In this test, your doctor will physically assess urinary tract system. The doctor will check for the following
- Large and tender prostate and bladder
- Discharge from the urethra
- Lower urine stream
- Swellings and redness on the penis
A number of tests can also be done to help diagnose urethral stricture. They include
Cystoscopy
This a surgical procedure conducted to check inside of your bladder and urethra using a telescope. There are two types of cystoscopy your doctor can use: flexible and standard or rigid cystoscopy.
In this procedure, your doctor cleans your urethra and applies an anesthesia on the inside of your urethra to the numb the area and you comfortable. Cystoscopy is then put in the urethra until it reaches the bladder.
A saline solution flows through the tube to fill your bladder. Your doctor will ask to describe how you feel when saline solution flow through the bladder. Your answers will help the doctor know more about your condition.
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is an examination of urine to determine components in the urine. Your doctor will tell you to collect a certain sample of urine. The sample will be analyzed in the laboratory to check for blood in the urine and infections.
Urine flow rate test
Your doctor will perform test to determine the rate of urine flow. The doctor will ask you to pass urine and determine the amount of urine passed per second.
Sexually transmitted infections test
Your doctor will take a sample of your urine and analyze it for sexually transmitted infections such as gonorrhea and Chlamydia.
Urine culture
This is a test conducted to check for bacteria and other microorganisms in the urine. Your health provider uses a catheter to collect a sample of your urine and analyses it. This test is done if you are suspected to have a urinary tract infection. Presence of bacteria or yeast in the urine may indicate you have a urinary tract infection.
Treatment
Urethra stricture can be corrected using the following treatment options
Cystoscopy
This procedure can be used to widen the stricture and correct the problem. During this procedure, anesthetizing medicine is applied on the area of operation to reduce pain. The scope is then inserted into your urethra and enlarges your urethra.
Surgery
Surgery can be used if stretching the urethra cannot correct the problem. Surgery depends on place and the extent of the stricture; if the constricted area is short and away from the muscles that control the bladder, the stricture can remove or enlarged.
A type of surgery called open urethroplasty is used to correct longer and painful strictures. In this procedure your doctor removes the affected area reconstructs the urethra.
In severe cases, especially when your bladder is completely damaged, urine diversion is necessary. Your surgeon can perform surgery to channel urine through a hole in your abdomen .Then uses part of your intestines to link the opening to the ureters.
Use of catheter
A tube called catheter can be placed in your urethra to drain out urine. Catheter can irritate your bladder and cause urinary tract infections.
There is no known way of preventing urethral stricture unless it is caused by sexually transmitted infections. Use protection while having sex can minimize some cases of urethral stricture. It is vital to seek medical attention if you are experiencing the above symptoms of urethral stricture.
Reference List
- Urethral Stricture – http://www.healthline.com/health/urethral-stricture#overview1
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001271.htm
- http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/450903-overview#a11
- http://www.urologyhealth.org/urologic-conditions/urethral-stricture-disease
- http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/urethral-stricture/basics/definition/con-20037057
- Urethral Stricture https://patient.info/health/urethral-stricture-leaflet
- Urethral Stricture in Men – https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/urethral-stricture-in-men
