Mandibular Fossa
What Is Mandibular Fossa?
Mandibular fossa is a section in the temporal bone of your skull. It is responsible for closing and opening of your mouth, which is known as mastication. It is here where the mandible head is able to interact with the articular disc. 1
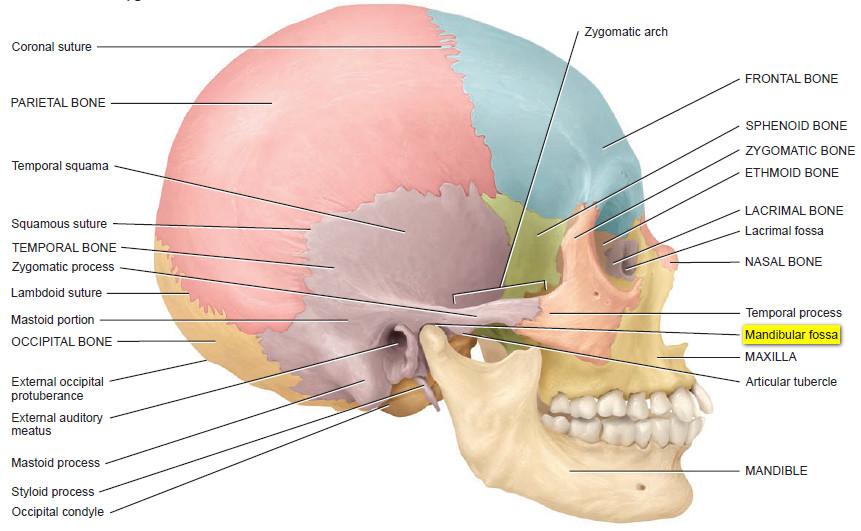
Petrotympanic fissure divides mandibular fossa into two sections: anterior and posterior. The anterior section attaches to the mandibular condyle and is the largest between the two. It covers the external acoustic meatus.
Posterior has parotid gland and is separated from tympanic plate by squamotympanic fissure.
Function
Mandibular fossa plays key role in chewing. Mandibular fossa, mandibular condyle and articular tubercle are part of your temporomandibular joint (TMJ).
These structures enable you to open and close your mouth as well as move it forward, backward or to the sides.
Temporomandibular Joints
The human skull has two temporomandibular joints (TMJ) that attach the skull to the mandible (lower jaw bone). They also help in opening and closing of the mouth.
The joint has fibrous connective tissue and is surrounded by fibrous capsule. The joint cavity is divided into inferior and superior section by the articular disc.
It is in the superior section where mandible gliding movements occurs; opening and closing of the mouth .The inferior section supports the mouth to move back, forward or sides; this is called hinge movement.
Apart from tissues, the joint comprises of muscles to assist in chewing or mastication process. These muscles include temporalis, medial, lateral pterygoids and masseter.
These muscles emanate from first pharyngeal arch and have third branch nerves of trigeminal and mandibular. It also has numerous ligaments that connect the mandible to sphenoid and temporal bone.
Mandibular fossa enables you to open, close and move your mouth back, forward and to the sides. When mandibular fossa and other structures involved in chewing are damaged, your eating is affected. The following conditions can damage mandibular fossa:
Tempromandibular Joint Disorders
Tempromandibular Joint disorders are a group of diseases that affect tempromandibular Joint and its nearby structures such as blood vessels, ligaments and tendons. These disease cause pain and disrupts the function of the joint.
These disorders are grouped into the following categories: myogenous and arthrogenous.
Myogenous disorder
This disorder is also called masticatory myalgia and is associated with pain due to problems in muscles that support chewing. Muscle problems that can cause this disorder include muscle spasm, muscle contracture and myofascial pain.
Muscle spasm also called seizures is where your muscles contracts involuntary for a short time. Muscle spasm may occur when you overstretch a weak muscle or injury to the muscles.
Myofascial pain occurs in soft areas of your muscles such as ligament, tendons and muscles in the skeleton. Pain can also spread to other muscles such as temporalis.
Arthrogenous
Myositis is a condition that causes muscles and connective tissues to become swollen and inflamed. The swelling and inflammation can be confined in certain areas or generalized over your muscles.
The inflammation can occur due to drugs or overstretching. Infections especially those from your gums as well as injury to your teeth can cause swelling and pain in your chewing muscles.
Diseases also can cause arthrogenous disorder. They include:
Degenerative joint disease
This is a disease that causes the cartilage in your joints to become swollen, inflamed and breaks away. It is also called osteoarthritis. This disease is very common and affects many people globally. Age and natural process of wear and tear in your body can give rise to osteoarthritis.
However, other risk factors can increase your chances of developing degenerative joint disease. These factors include:
- Carrying of heavy materials frequently or making tiring movements. People doing manual labor and other physical activities are prone to this disease.
- It can also result from birth. A child born with abnormal joints may develop this disease.
- People who are too heavy or obese can exert pressure on their joints which can lead to damage to the cartilage in the joint.
- Injury to joints from accidents may also cause this condition. These injuries can damage the bones in your joints which increases your vulnerability to the degenerative joint disease.
- Eating food that lack vital nutrients and minerals such as vitamins, calcium, and magnesium can lead to weak muscles and bones in the joints. The weak bones and tissue can easily break away when under pressure.
Rheumatoid arthritis
This is a disease that occurs due to a hyperactive immune system which attacks and destroys your healthy body tissues and organs.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a type of autoimmune disease. Normally, your immune system has antibodies that protect your body against harmful antigens.
Once you have an autoimmune disease, your immune system antibodies attack and destroy tissues in your joints, which lead to swelling and inflammation. This disease can spread and affect many joints in your body.
Other diseases that affect your joints include:
- Ankylosis
- Neoplasia
Diagnosis
A thorough physical examination of your mandible and surrounding structures for swellings, tenderness, redness and movement of the mandible is necessary to detect issues with mandibular fossa.
Other tests such as X-rays and CT scan can be used to provide detailed images of your ligaments, bones, tendons and other muscles. MRI scan is used to check problems with the joint disc. These images can help in planning and managing problems in mandibular fossa.
Treatment & Management
Problems that affect mandibular fossa and surrounding tissues can be managed through the following techniques:
- Patients with loose teeth or gum infections can see the dentist for treatment.
- Antibiotics can be recommended to lower the risk of infection
- Muscle relaxants are used to help reduce pain in the chewing muscles.
- Pain killers and anti-inflammatory drugs can assist in relieving pain and inflammation in the mandibular fossa and nearby structures.
- Regular stretching exercises are effective in strengthening your jaw muscles.
- Injecting corticosteroid into your joints reduces pain.
Surgery can be used if other methods are ineffective in treating the problem. Various surgery procedures can be done such as:
Arthrocentesis
In this procedure, your doctor inserts a needle into your Tempromandibular Joint and removes fluids and other deposits. This can help reduce pain and inflammation.
Open-joint surgery
This procedure is used if the joint structure is the cause of the problems in the joint. In this method, the doctor can perform surgery to repair or replace the joint depending on the severity of the damage in the joint.
This procedure has many side effects and your doctor will discuss with you the risks and benefits of open-joint surgery.
If you have mandibular fracture, seek urgent medical attention because fractures can obstruct your airways leading to serious complications2.
Reference List
- Mandibular Fossa. Available at http://healthfixit.com/mandibular-fossa/
- Mandibular fractures. Available https://patient.info/doctor/mandibular-fractures-and-dislocations
- Degenerative Joint Disease. Available at https://spinecare.luminhealth.com/conditions/degenerative-joint-disease/
- Temporomandibular joint disorder. Available http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tmj/home/ovc-20209398
- Mandibular fossa. Available at https://www.imaios.com/en/e-Anatomy/Anatomical-Parts/Mandibular-fossa
- Tempromandibular Joint Disease (TMJD). Available at https://www.cedars-sinai.edu/Patients/Programs-and-Services/Pain-Center/Head-and-Neck-Pain/Tempromandibular-Joint-Disease-TMJD.aspx
- Temporomandibular Disorders. Available at http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1143410-overview#a6
