Ingrown Pubic Hair
What is Ingrown Pubic Hair?
Ingrown Pubic Hair is ingrown when – after waxing, sugaring, plucking or shaving – it exits the skin sideways (at an abnormal angle) and curls back under the skin instead of growing normally.
The ingrown hair results in the formation of painful bumps that are itchy and susceptible to infection. People with coarse and curly pubic hair are more likely to suffer ingrown hair than those with fine and thin pubic hair.
For men ingrown pubic hair can occur on the penis or scrotum and for women it can occur on the labia or vagina. 1,4
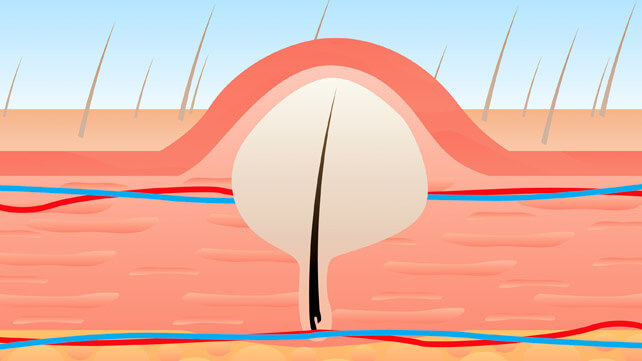
Causes
Ingrown pubic hair is mostly caused by aggressive hair removal methods like waxing, plucking, sugaring or shaving. These methods at time leave a short hair that curls back into the skin instead of growing outwards.
Pubic hair can also become ingrown if one wears very tight clothing that irritates the pubic area and cause the clogging of the hair follicles due to build up of sweat, dead skin, sebum and debris.
Some sex hormones during pregnancy or birth can trigger excessive hair growth that makes one more susceptible to ingrown pubic hair.
Caesarean sections (a surgical method of delivery for pregnant women) can cause ingrown pubic hair as some mothers complain of small bumps with dark centres at some point on the scar line.
Symptoms
Where an ingrown pubic hair has developed, an individual may notice the following symptoms:
- Small, hard and round bumps referred to as papules or some small pus-filled bumps referred to as pustules. These sites usually look like pimples but are red, swollen, itchy and can be painful.
- In some cases the bumps cause redness, inflammation and itchiness around the ingrown hair.
- For some cases the skin around an ingrown pubic hair may become darker; it is called hyperpigmentation.
Diagnosis
- If you have not recently used a hair removal technique on the area with the ingrown pubic hair your doctor may need to further test you for any underlying cause of the ingrown pubic hair.
- If you often suffer ingrown pubic hairs or excessive and abnormal growth of pubic hair, schedule a doctor’s appointment to get prescribed a lasting solution.
Treatment
For most people ingrown pubic hairs clear up on their own without needing any treatment. If the ingrown pubic hair does not grow back out through the skin, try one of these methods listed here:
- Infected ingrown pubic hairs are usually treated with creams but in case of severe infection the doctor may prescribe oral antibiotics like Neosporin.
- In cases where ingrown pubic hairs do not come out naturally and cause a lot of irritation, the dermatologist can use surgery to remove them. The disadvantage of surgery is the dark marks or scars usually formed after.
- Do not perform further hair removal in the affected area. Any hair removal methods shall worsen the sensitive area.
- Resist the urge to scratch the affected area. This not only heighten discomfort by irritating the skin, but also puts you at risk for infection and development of a scar.
- Use warm compresses on the area to ease pain and the itchy sensation. Rub a clean wet cloth over the area in a circular motion for ten to fifteen minutes. This softens the ingrown pubic hair and eases it out from under the skin.
- Using a pair of sterile tweezers or needle, gently pull at the ingrown hair without plucking it out entirely until the area is healed as the skin may heal over the hair. Take caution not to break through your skin hence risk infection
- Remove the dead skin around the ingrown hair by gently washing and exfoliating to aid the hair return to the skin surface. Sometimes doctors maybe prescribe a medication to help dead skin cells shed away more quickly.
- Steroid creams can be used to ease discomfort if the area around the ingrown hair is excessively red, inflamed and itchy.
Prevention
Development of ingrown pubic hair can only be prevented by:
- Not using aggressive hair removal methods like waxing, shaving and plucking. Instead one should opt for chemical hair removers if their skin is not extremely sensitive,. Laser hair removal and electrolysis are more permanent hair removal methods that destroy the hair shaft at the root and they usually require several treatments that are spread out over the course of weeks or months.
- Avoiding wearing extremely tight clothing that may irritate the crotch and cause ingrown pubic hairs.
- If one insists on shaving and other aggressive hair removal methods the risk of ingrown hair can be prevented by:
- Using a sharp and preferably new razor when shaving.
- Trim the longer portions of hair with and electric trimmer or manicure scissors in order to making shaving easier.
- Soak in a warm shower or bath for five to ten minutes to soften the pubic hair. Wet and soft hair is unlikely to curl into the skin compared dry coarse and curly hair.
- Applying a pre-shave lotion or oil softens the hair and offer some protection from friction.
- Use proper shaving foam or cream that is thick and has a heavy lather that is designed to protect the skin.
- Always shave in the direction of hair growth to prevent irritation .
- Use an after shave that contains glycolic or salicylic acid which prevent pimples, ingrown hairs, razor burns and irritation.
Home Remedies
- Tea tree oil kills alleviates inflammation of the sensitive area and also kills bacteria that may cause infection. Mix the oil with water for dilution and apply on the affected area using a cotton ball.
- Sugar serves as a natural exfoliator and when mixed with olive oil or honey, the paste can be applied on the skin in circular motions and rinsed off with warm water.
- Baking soda can be mixed with water and applied to the skin using a cotton ball and then rinsed off with cold water. This treatment exfoliates the skin and alleviates inflammation at the area around the ingrown pubic hair.
Complications
If the area surrounding the ingrown pubic hair becomes infected on may notice the following:
- If scratched, popped, squeezed, broken or otherwise irritated bumps around ingrown pubic hairs may form pus filled blisters or lesions due to damage of the skin structure and entry of bacteria.
- Development of a cyst with a black or red dot in the centre.
- People prone to fungal and bacterial infections may develop a boil or abscess in the sensitive area.
- If ingrown hair becomes infected it becomes painful and gets filled with pus.
- Bleeding or oozing of pus may also occur as a result of infection if the bump is squeezed or popped.
Reference List
- Here’s How to Prevent Ingrown Pubes Once and For All. Retrieved from Women’s Health: https://womenshealthmag.com/beauty/ingrown-pubic-hair
- Treating and Preventing Ingrown Pubic Hair. Retrieved from Healthline – https://healthline.com/health.treating-preventing-ingrown-vaginal-hair
- How to Treat Ingrown Hairs in the Pubic Area. Retrieved from Livestrong – https://livestrong.com/article/180781-how-to-treat-ingrown-hairs-on-thepubic-area/
- How to Get rid of Ingrown Pubic Hair on Male, Female Bikini Area. Retrieved from Treat, Cure Fast – https://treatcurefast.com/hair/pubic-ingrown-hair/ingrown-pubic-hair-infected-cyst-bump-get-rid-treat-remove-prevent-pubic-area-ingrown-hair-boil/
- Ingrown Pubic Hair: What are the Causes and How to Get Rid if it Fast. Retrieved from Express – https://express.co.uk/life-style/life/768412/ingrown-pubic-hair
